What is CHEAQS?
CHEAQS Next is a computer program for calculating CHemical Equilibria
in AQuatic Systems. You supply input data, the program calculates the
chemical speciation for you. CHEAQS Next is free.
Features
- You can calculate the concentration of complexes, but you can also calculate:
- redox equilibria;
- complexation by natural organic matter (three different models
developed by Tipping and co-workers: Model V, Model VI and Model
VII);
- solids that are formed due to oversaturation (or just calculate if they are oversaturated or not);
- adsorption (surface complexation model).
- pH: you can either specify a fixed pH or have the program calculate the pH for you.
- Input: you can edit input interactively or read from an input file.
- Output: you can view output on your screen, save in an output file, or export to an .CSV or .XML file.
- You can perform calculations with the Mean Spherical Approximation model (MSA), a model to calculate activities, also at high salt concentrations, with a good theoretical basis.
- You can perform 'titrations' and 'calibrations'.
- You can customize the database.
Database
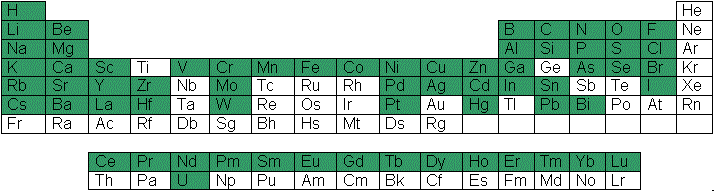
CHEAQS Next comes with a large database. Documentation is available for each equilibrium reaction in the database so you can always trace the source of an equilibrium reaction. In the periodic table on the right, you can see (in green) which elements are covered in CHEAQS Next' database. The database contains:
- 53 cations (H+, Li+, Be2+, Na+,
Mg2+, Al3+, K+, Ca2+, Sc3+,
Cr3+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Co2+,
Co3+, Ni2+, Cu+, Cu2+, Zn2+,
Ga3+, Rb+, Sr2+, Y3+, Zr4+,
Pd2+, Ag+, Cd2+, In3+, Sn2+,
Sn4+, Cs+, Ba2+, La3+, Ce3+,
Pr3+, Nd3+, Pm3+, Sm3+, Eu3+,
Gd3+, Tb3+, Dy3+, Ho3+, Er3+,
Tm3+, Yb3+, Lu3+, Hf4+,
 Pt2+, Hg2+, Pb2+,
Bi3+, U(VI)O22+);
Pt2+, Hg2+, Pb2+,
Bi3+, U(VI)O22+); - 54 ligands including 20 amino acids (OH-, H2BO3-, CO32-, NH3, NO2-, NO3-, F-, H2SiO42-, PO43-, S2-, SO32-, SO42-, Cl-, VO43-, CrO42-, MnO4-, H2AsO3-, AsO43-, SeO32-, SeO42-, Br-, MoO42-, I-, WO42-, CN-, acetate, catechol, salicylate, phthalate, NTA, citrate, HEDTA, EDTA, DTPA, glycine, alanine, serine, proline, valine, threonine, cysteine, isoleucine, leucine, asparagine, aspartate, glutamate, glutamine, lysine, methionine, histidine, phenylalanine, arginine, tyrosine and tryptophan);
- 2708 complexes;
- 273 solids;
- 81 adsorption equilibria (as calculation examples);
- 16 redox equilibria (for Fe, Co, Cu, Sn, Cr, Mn, Pb, N, S, As and Se);
- 4 gases (CO2, NH3, H2S, SO2);
- organic complexation according to the models of:
- Tipping et al. (Environmental Chemistry, 2011), also known as Model VII;
- Tipping (Aquatic Geochemistry, 1998) also known as WHAM-6;
- Tipping & Hurley (GeoChim. CosmoChim. Acta, 1992); Tipping (Comp. GeoSc., 1994) also known as WHAM or Model V;